Decoding the Complex Gut-Brain Connection
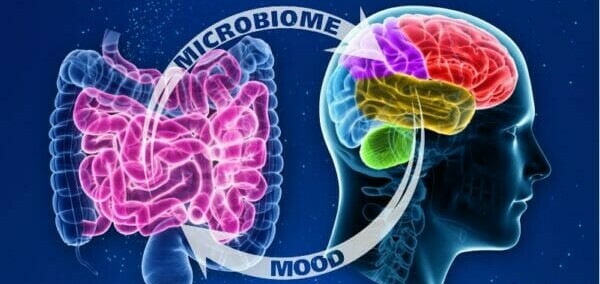
The human body is a complex and interconnected system, where seemingly far-flung organs and systems communicate and influence each other in profound ways. One such fascinating connection is the gut-brain axis, a network of pathways linking your gut and your brain. This emerging field of research sheds light on the surprising influence your gut health has on your overall well-being, including your mood, cognitive function, and even risk of certain diseases.
How the Brain Talks to Your Gut
The gut-brain axis is a two-way street. The vagus nerve, the longest cranial nerve, acts as the main communication channel between the brain and the gut. It carries signals from the brain to the gut, influencing digestion, motility, and immune function. Conversely, the gut sends signals back to the brain through the vagus nerve and other pathways, such as the immune system and the production of hormones.
Ignoring the gut-brain dialogue can have significant consequences. Studies have shown a link between disruptions in the gut microbiome (the community of trillions of bacteria living in your gut) and various health problems, including anxiety, depression, chronic fatigue, and even neurological disorders.
Beyond Probiotics: A Holistic Approach to Gut Health
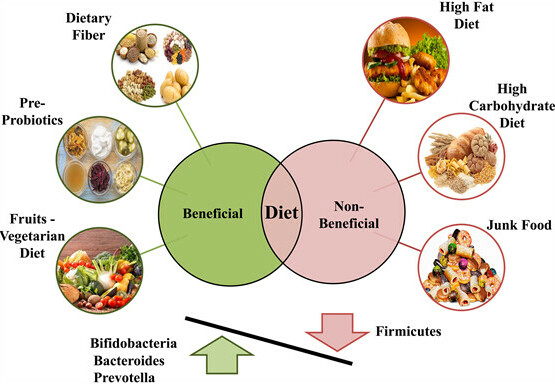
Probiotics, live microorganisms with potential health benefits, have become a popular focus in gut health discussions. However, a holistic approach goes beyond simply adding probiotics to your diet. A balanced diet rich in fiber, prebiotics (the food source for gut bacteria), and essential nutrients is crucial.
Nutrient deficiencies, particularly vitamins A, C, D, and B vitamins, can negatively impact digestion and overall gut health. Additionally, addressing underlying digestive disorders like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is essential for maintaining a healthy gut-brain connection.
The key to unlocking optimal gut-brain health lies in a comprehensive strategy that encompasses:
- Diet: Prioritize a balanced, fiber-rich diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented foods.
- Lifestyle: Manage stress through techniques like meditation or yoga, prioritize adequate sleep, and engage in regular exercise.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can disrupt the delicate balance of gut bacteria, leading to inflammation and impacting mood. Practicing stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can be incredibly beneficial.
Harnessing Lifestyle Changes for Gut-Brain Harmony
Several lifestyle modifications can significantly improve your gut-brain health: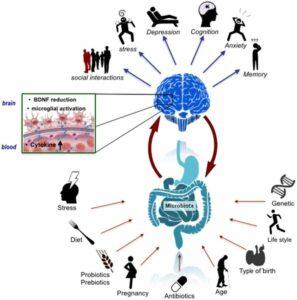
- Manage Chronic Stress: As mentioned above, chronic stress can wreak havoc on your gut bacteria. Implementing stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can alleviate stress and promote gut health.
- Prioritize Sleep: Sleep is crucial for overall health, and maintaining a regular sleep schedule is vital for gut health as well. Adequate sleep allows your body to rest and repair, including your gut microbiome.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation: Incorporating mindfulness practices like meditation or spending time in nature can promote relaxation and improve gut health. These activities can help reduce stress and create a calmer internal environment for your gut bacteria to thrive.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity not only benefits your physical health but also your gut health. Exercise promotes gut motility, circulation, and overall well-being, contributing to a healthy gut-brain axis.
Cultivating a Healthy Gut Ecosystem: Practical Tips
While the gut-brain connection is complex, several practical steps can support a healthy gut ecosystem:
- Embrace Fermented Foods: Incorporate fermented foods like yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha into your diet. These foods contain beneficial bacteria that can positively impact your gut microbiome.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting a healthcare professional can help you develop a personalized approach to gut health. They can address any underlying digestive issues, recommend dietary modifications, and guide you towards appropriate supplementation if needed.
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Good hygiene practices like washing your hands regularly and maintaining food safety can help prevent harmful bacteria from entering your gut and disrupting the delicate balance of your gut microbiome.
The Benefits of Long-Term Commitment
Investing in your gut health is an ongoing journey, but the rewards are substantial. By implementing the practices mentioned above and making gut health a priority, you can cultivate a healthy gut-brain connection, potentially leading to improved mood, cognitive function, increased energy levels, and a reduced risk of various health problems. Remember, consistency is key: by making these changes a part of your daily routine, you can pave the way for a healthier and happier you.